-
8.Conclusion
-
10.Final Thoughts
In this article, we will provide an in-depth guide to laser cutting, explaining how it works, what materials it can cut, its advantages and limitations, and how you can integrate it into your manufacturing process. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of what laser cutting is and how it can benefit your industry.
What is Laser Cutting?
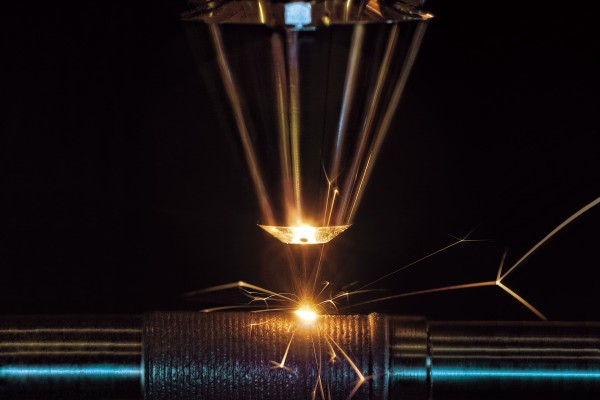
Laser cutting is a process of cutting materials using a laser beam. The laser beam is generated by a laser source and focused onto the material by a lens or mirrors. The intense heat of the laser beam vaporizes or melts the material, allowing it to be cut with precision.
Laser cutting can be used to cut a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, fabric, and paper. It is particularly useful for cutting complex shapes and patterns, as well as for creating intricate designs.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Laser cutting works by using a laser beam to heat and vaporize the material. The laser beam is focused onto the material using a lens or mirrors, creating a high-intensity heat source that melts or vaporizes the material. The laser beam is controlled by a computer program that determines the shape and size of the cut.
The laser cutting process can be divided into several steps:
- Designing the cut: The first step is to design the cut using a computer-aided design (CAD) software. This software creates a digital file that contains the instructions for the laser cutting machine.
- Preparing the material: The material to be cut is prepared by cleaning and drying it. The material is then placed on the laser cutting bed.
- Focusing the laser: The laser beam is focused onto the material using a lens or mirrors. This creates a high-intensity heat source that melts or vaporizes the material.
- Cutting the material: The laser beam is moved across the material, cutting it according to the design. The laser cutting machine is controlled by a computer program that ensures the accuracy and precision of the cut.
What Materials Can Laser Cutting Cut?
Laser cutting can be used to cut a wide range of materials, including:
- Metals: Laser cutting can cut a variety of metals, including stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass.
- Plastics: Laser cutting can cut plastics such as acrylic, polycarbonate, and ABS.
- Wood: Laser cutting can cut a variety of woods, including MDF, plywood, and balsa wood.
- Fabric: Laser cutting can cut fabrics such as cotton, silk, and polyester.
- Paper: Laser cutting can cut paper and cardstock.

What are the Advantages of Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting offers several advantages over traditional cutting methods, including:
- Greater precision: Laser cutting offers greater precision than traditional cutting methods, allowing for more intricate designs and shapes.
- Faster cutting speeds: Laser cutting is faster than traditional cutting methods, reducing production time and costs.
- Reduced waste: Laser cutting produces less waste than traditional cutting methods, reducing material costs and environmental impact.
- Versatility: Laser cutting can be used to cut a wide range of materials, making it a versatile tool for manufacturing.
What are the Limitations of Laser Cutting?
While laser cutting offers many advantages, it also has some limitations, including:
- Material thickness: Laser cutting is most effective on materials up to 1 inch thick. Thicker materials may require multiple passes, reducing cutting speed
- Material type: Laser cutting is not effective on all materials. Some materials, such as reflective or transparent materials, cannot be cut effectively using a laser.
- Cost: Laser cutting machines can be expensive to purchase and maintain, making it less accessible for some industries.
- Safety: Laser cutting can pose a safety hazard if proper precautions are not taken, including proper ventilation and personal protective equipment.
Integrating Laser Cutting into Your Manufacturing Process
If you are considering integrating laser cutting into your manufacturing process, there are several steps you can take to ensure a smooth transition:
- Identify your needs: Determine what materials and shapes you need to cut and what level of precision is required.
- Research your options: Research different laser cutting machines and suppliers to find the best fit for your needs and budget.
- Train your staff: Provide training to your staff on how to operate and maintain the laser cutting machine safely and effectively.
- Monitor your results: Monitor the quality of the cuts and adjust the settings as needed to achieve the desired results.
Examples of Laser Cutting Applications
Laser cutting has many applications across a wide range of industries. Here are a few examples:
- Aerospace: Laser cutting is used to cut complex shapes and patterns in aircraft parts.
- Automotive: Laser cutting is used to cut parts for engines, transmissions, and other components.
- Electronics: Laser cutting is used to cut and shape electronic components such as circuit boards.
- Signage: Laser cutting is used to create intricate designs for signs and displays.
- Fashion: Laser cutting is used to cut fabrics for clothing and accessories.
Conclusion
Laser cutting is a powerful tool that offers precision, speed, and versatility in cutting a wide range of materials. While it has some limitations, it has become an indispensable tool for many industries. By understanding how laser cutting works, what materials it can cut, and its advantages and limitations, you can make an informed decision about integrating it into your manufacturing process.
Key Takeaways:
- Laser cutting is a process of cutting materials using a laser beam.
- Laser cutting can be used to cut a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, fabric, and paper.
- Laser cutting offers several advantages over traditional cutting methods, including greater precision, faster cutting speeds, reduced waste, and versatility.
- Laser cutting has some limitations, including material thickness, material type, cost, and safety.
- To integrate laser cutting into your manufacturing process, identify your needs, research your options, train your staff, and monitor your results.
Final Thoughts
Laser cutting is a powerful tool that offers precision, speed, and versatility in cutting a wide range of materials. While it has some limitations, its advantages have made it an indispensable tool for many industries. By understanding how laser cutting works, what materials it can cut, and its advantages and limitations, you can make an informed decision about whether to integrate it into your manufacturing process. As with any new technology, it is important to do your research, train your staff, and monitor your results to ensure that you are getting the most out of this powerful tool.
Quickscout
Looking for suitable
technology providers?
Start scouting!